Workforce planning: Strategies, models & tools
Skills shortages, rising labour costs, and disruptive technologies reshape how organisations think about talent. HR teams must go beyond short-term hiring needs to understand future skill requirements and workforce dynamics, driving effective workforce planning across the organisation.
Liam Clark

Workforce planning is important because it ensures human resources are aligned with business goals, supports strategic decision-making, reduces costs, and improves overall workforce efficiency. Let's examine the importance of workforce planning, the models that underpin it, and the tools that make it actionable.
Workforce planning has become a critical function for organisations seeking to align talent with long-term strategy while remaining agile in uncertain markets. Without a structured approach, companies risk costly inefficiencies, compliance challenges, and missed growth opportunities. By integrating data-driven models, modern tools, and clear frameworks, workforce planning transforms HR from a reactive function into a strategic partner. Business leaders play a key role in aligning workforce planning activities with organisational strategy and making informed decisions to support long-term business success.
What is workforce planning, and why is it important?
Workforce planning concerns matching the labour needs of organisations with the individuals who can perform those tasks. This task falls to the HR department to analyse the current workforce and determine future workforce requirements in line with organisational goals. Workforce planning should be integrated with the overall organisational strategy, ensuring that workforce planning aligns with broader business objectives and market trends. With planning, organisations achieve 'the four rights': the right employees in the right role on the right contract and at the right cost, as workforce planning aligns human resources strategies with organisational success.
Traditional vs strategic workforce planning
HR experts differentiate between traditional and strategic workforce planning. Comparing the two approaches highlights the shift from reactive to proactive management:
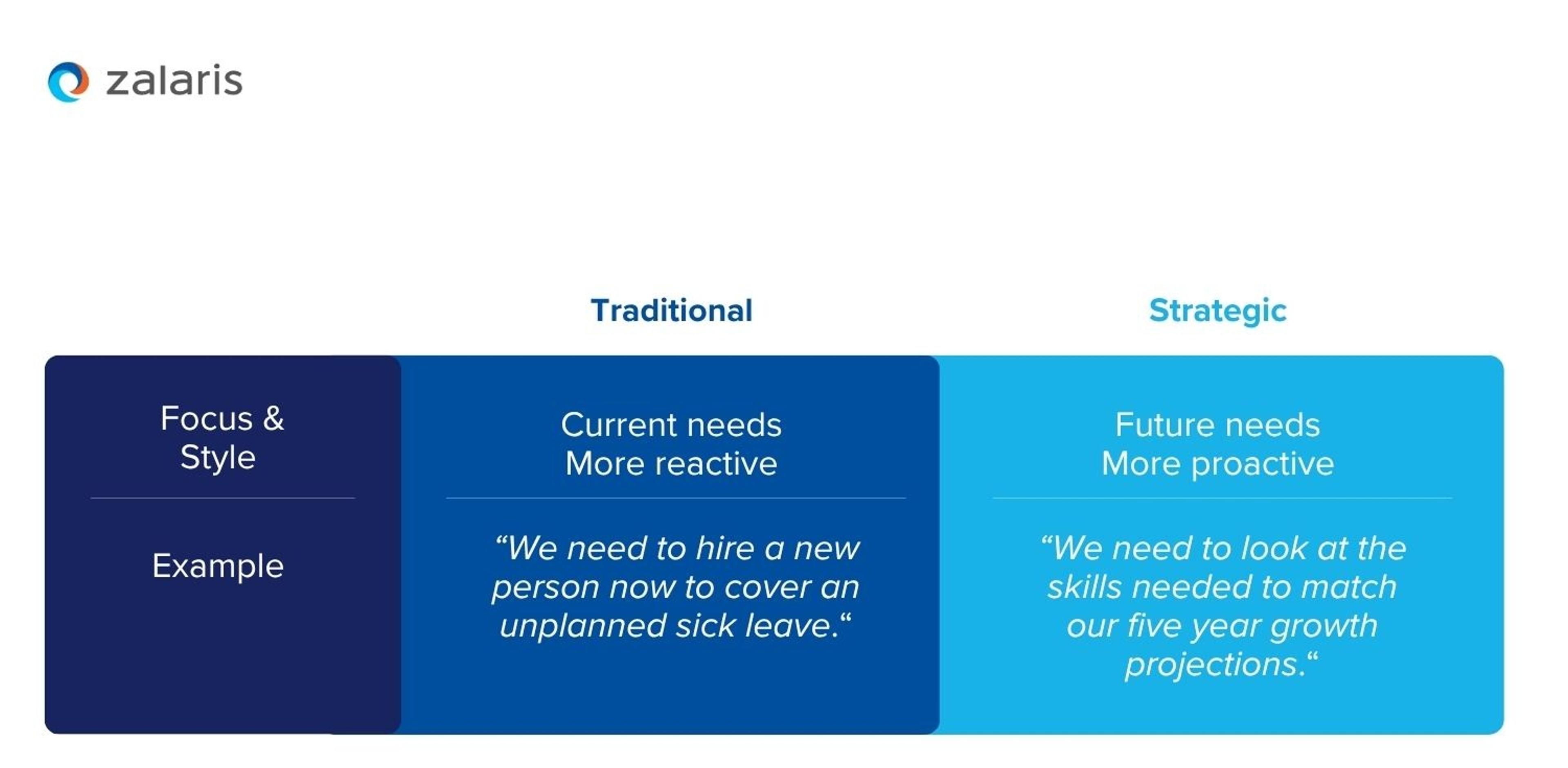
A strategic approach embeds people strategy in the wider business strategy. With it, organisations better understand the potential skill gaps that may arise as the business develops, and the value of reskilling or recruiting before problems occur.
Why does workforce planning matter?
According to a PwC survey, 47% of HR leaders rank talent retention and skills shortages among the top three barriers to delivering on their HR strategy. With workforce planning, organisations can better respond to these barriers. Workforce planning helps organisations anticipate workforce changes, align resources, and ensure they are prepared for future demands.
With a strategic approach, organisations unlock the benefits of workforce planning that:
- Align talent with business strategy: HR teams can prepare for future expansion plans, product, or service line-up changes, and industry changes. This includes forecasting future staffing needs and the ability to anticipate future staffing requirements based on industry trends and market demand.
- Manage labour costs: Teams gain visibility into staffing needs, making it easier to reduce labour costs via better scheduling, redeployment, and resource forecasting.
- Improve productivity and performance: Mapping skills ensure employees work in roles where they add the most value, eliminating mismatches in skills and workload and boosting productivity.
- Reduce turnover and talent risk: Retirements, promotions, and job changes are an inevitable part of an organisation’s employment lifecycle and can be costly. According to Gallup, organisations may spend up to 200% of a leader’s annual salary to replace them, around 80% for professionals in technical roles, and about 40% for frontline employees. By planning for these inevitabilities, organisations can reduce both the time and cost of rehiring, while maintaining productivity and continuity.
- Strengthen compliance and risk management: A structured plan helps organisations adhere to local employment laws and regulations, avoiding costly compliance failures. For instance, in the healthcare sector alone, 45% of compliance leaders report increased pressures and expectations from leadership and the Board regarding the compliance programme.
- Enable agility in a changing world: Technologies such as AI have rapidly transformed the way we work, resulting in job losses and the emergence of new job roles. Resilient organisations with workforce plans can respond to these changes.
Workforce planning foundations: Models, frameworks, and the planner
Effective workforce planning relies on models, frameworks, and the expertise of workforce planners. Models help organisations anticipate future needs and identify skill gaps, and are essential to identify skills gaps within the workforce so that targeted training and resource allocation can be implemented. Frameworks turn these insights into actionable plans, and workforce management tools can automate and support the planning process by improving efficiency and leveraging technology for better decision-making. Workforce planners ensure these plans are executed effectively. Focusing on these key elements is crucial for successful workforce planning.
The models
Workforce planning isn’t a one-size-fits-all activity. Several models and strategies exist to enable organisations to select those that best align with their organisational goals. Aligning the operational workforce with immediate business needs is crucial for effective resource allocation and adapting quickly to market changes.
| Workforce planning model | The approach | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| The Supply and Demand Forecasting Model | Compares future labour demand with projected workforce supply. Incorporates operational workforce planning to ensure short-term resource allocation meets immediate business needs. | Identifies shortages or surpluses early, supporting smarter hiring and training. |
| The Strategic Workforce Planning (SWP) Model | Ties workforce planning directly to long-term business strategy. | Aligns workforce capability with growth and digital transformation. |
| The Scenario Planning Model | Tests workforce needs under multiple “what if” situations, including economic downturn, mergers, etc. | Builds resilience and reduces disruption risks. |
| The Skills Gap Analysis Model | Maps current skills against future requirements. | Guides reskilling and hiring in an era of automation. |
| The Zero-Based Workforce Planning (ZBWP) Model | Requires every role to be justified from scratch based on future needs. | Eliminates inefficiencies and encourages innovative role design. |
Effective workforce planning not only addresses immediate operational workforce needs but also supports the organisation’s strategic plan by aligning talent initiatives with long-term objectives.

The role of the workforce planner
Workforce planners play a central role in making a framework operational. They translate strategy into actionable workforce priorities, analyse data to identify gaps, model future scenarios, and coordinate strategies that ensure workforce decisions directly support long-term business outcomes. Dedicated workforce planning teams, often led by management or HR departments, are responsible for overseeing these strategic workforce planning activities, especially during significant business changes. Line managers are also involved in executing workforce plans and resourcing strategies, ensuring that decisions made in the planning process are effectively implemented. Essentially, they act as the bridge between strategic planning and workforce execution.
The results inform resourcing plans and guide staffing decisions, ensuring that workforce planning outcomes directly shape how resources are allocated to meet organisational needs.
Creating a strategic workforce planning framework: A practical lesson for workforce planners
While the choice of model depends on industry, business size, and goals, most effective strategic workforce planning frameworks follow the same five steps. This offers a workforce planner both a clear structure for analysis and the foundation to turn insights into practical, actionable decisions.
When forecasting future workforce scenarios, it is essential to consider and prepare for future challenges that may impact workforce needs and organisational objectives.
In the step focused on closing gaps with targeted strategies, implementing solutions to address identified staffing requirements is crucial to ensure the achievement of strategic goals.
As a best practice, organisations should also identify and address factors that may hinder strategic change during workforce planning to support successful implementation of new initiatives.
The strategic workforce planning framework:
The following strategic workforce planning framework provides a structured approach:
- Anchor planning to business strategy: Workforce planning must directly align with business objectives, whether that involves growth, transformation, or new market entry.
- Scan the internal and external environment: Combine analysis of internal workforce demographics, structure, and attrition with external factors such as market shifts, emerging technologies, and regulation.
- Assess the current workforce with data: Utilise detailed audits and workforce analytics to gain a comprehensive understanding of headcount, skills, succession pipelines, and productivity.
- Forecast future workforce scenarios: Project needs under different possible futures, from business growth to disruption or automation. Identify which roles and skills will be critical in each scenario.
- Close the gaps with targeted strategies: Address shortages or surpluses through reskilling, recruitment, role redesign, succession planning, or diversity initiatives.
Turning framework into action: Best practices for the workforce planner
These best practices illustrate how a planner can apply this framework in practice:
- Turn insights into decisions: Use workforce data to make concrete choices affecting talent allocation, skills development, and succession.
- Prioritise strategic work: Automate or delegate transactional HR tasks to focus on planning and forecasting.
- Collaborate across functions: Ensure workforce plans support broader business objectives by working with finance, operations, and leadership.
- Plan for agility: Build flexible workforce scenarios that can adapt to organisational change, disruption, or new opportunities.
By combining the strategic framework with these best practices, a workforce planner can transform data into strategic decisions that strengthen organisational resilience and ensure the right people are in the right roles at the right time.

Gap analysis: Identifying workforce needs and priorities
Gap analysis is a cornerstone of the strategic workforce planning process, providing organisations with a clear understanding of where their current workforce stands in relation to future workforce requirements. By systematically comparing existing workforce capabilities with the skills, knowledge, and competencies needed to achieve strategic objectives, organisations can pinpoint critical skills gaps and prioritise their workforce needs.
This process begins with the collection and analysis of relevant workforce data, including performance data, employee demographics, and current skill sets. By evaluating this information against the organisation’s future needs and shaped by the strategic business planning process, HR teams can identify areas where the current workforce may fall short. This insight is essential for developing a workforce plan that addresses both immediate and long-term talent requirements.
A thorough gap analysis not only highlights where new skills are needed but also uncovers opportunities for upskilling, reskilling, or redeploying existing employees. By focusing on these priorities, organisations can ensure they have the right skills and workforce capabilities in place to support business objectives and drive future success. Ultimately, gap analysis transforms workforce data into actionable intelligence, enabling organisations to build a strategic workforce that is prepared to meet evolving business challenges.
Workforce planning tools: Increasing efficiency through technology
While workforce planning models provide the framework for thinking about workforce needs, technology enables organisations to put those models into practice with data-driven precision.
Human Capital Management (HCM) suites:
HCM platforms, such as Zalaris PeopleHub (powered by SAP SuccessFactors) centralise employee data, payroll, and performance records, making them the foundation for headcount and capacity planning. They help organisations understand how many people are available, where they are deployed, and whether this aligns with business demand.
Workforce analytics platforms:
Analytics software like Zalaris People Analytics transforms raw HR data into insights on skills availability, attrition risk, and workforce productivity. Its customised analytics dashboards combine payroll, time, and performance data for strategic decision-making. It is particularly powerful for conducting skills inventories and identifying gaps between today’s capabilities and future needs.
Scenario and forecasting tools:
Forecasting features within workforce management solutions, for example WorkAxle WFM, enable organisations to model workforce needs under various business scenarios, ranging from automation to rapid expansion or regulatory changes. Used for advanced scenario planning and forecasting, they help organisations prepare for growth and disruption alike.
With the right workforce planning technology, organisations can implement proven models, such as headcount planning, skills gap analysis, scenario planning, zero-based design, and succession planning. The most effective organisations use a combination of these tools and models to ensure that people strategies directly support long-term business outcomes.
Employee retention: Building a resilient workforce
Employee retention is a key pillar of strategic workforce planning, as it enables organisations to cultivate a stable and resilient workforce capable of supporting long-term business objectives. High retention rates contribute to a strategic workforce by reducing turnover costs, preserving institutional knowledge, and maintaining productivity - all of which are essential for sustaining a competitive advantage.
Strategic workforce planning helps organisations identify and address the factors that most influence employee retention. This includes conducting compensation and benefits analysis to ensure offerings are competitive, providing clear career development pathways, and fostering a positive work environment that supports work-life balance. By proactively addressing these areas, organisations can create a culture where employees feel valued and motivated to stay.
Effective employee retention strategies not only mitigate risks associated with talent loss but also help organisations deliver strategic value by ensuring continuity and stability within their teams. When workforce planning helps organisations retain top talent, it reduces the need for frequent recruitment and onboarding, allowing HR teams to focus on initiatives that drive business growth and achieve strategic objectives.
Action plan: Turning workforce planning into results
An actionable plan is essential for translating the insights gained from the strategic workforce planning process into measurable outcomes. Based on the results of the gap analysis, the action plan outlines the specific initiatives and strategies that will be implemented to address workforce needs and achieve strategic objectives.
Key components of an effective action plan include targeted strategies such as succession planning, talent development programs, and diversity and inclusion initiatives. Each initiative should be clearly defined, with assigned responsibilities and timelines to ensure accountability. To track progress and measure success, organisations should establish key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with both workforce planning efforts and the overall business strategy.
Regularly reviewing and updating the action plan is crucial to maintaining alignment with evolving business goals and market conditions. By making the action plan a living document, organisations can ensure their strategic workforce planning process remains dynamic and responsive, ultimately driving business success and delivering on strategic objectives.
Overcoming challenges in workforce planning
Strategic workforce planning is not without its challenges. Organisations often face obstacles such as skills gaps, talent shortages, and rapidly changing business environments that can hinder their ability to anticipate and meet future workforce needs. To overcome these challenges, agility and adaptability are essential.
Leveraging advanced workforce planning tools, such as scenario planning and predictive analytics, enables organisations to model different future workforce scenarios and prepare for a range of potential outcomes. This proactive approach helps organisations anticipate shifts in workforce demand and address skills gaps before they impact business performance.
Additionally, forming strategic partnerships with educational institutions, training providers, and industry organisations can help organisations access new talent pools and develop the skills needed to support future workforce requirements. By remaining flexible and continuously refining their workforce planning strategies, organisations can navigate uncertainty, mitigate risks, and ensure they have the strategic workforce needed to achieve their objectives.
Best practices for effective workforce planning
To maximise the impact of workforce planning, organisations should adopt a set of best practices that ensure alignment with their overall business strategy and strategic objectives. Regular gap analyses are essential for identifying and prioritising skills gaps, while targeted talent strategies help attract, retain, and develop the workforce needed for success.
Data-driven decision-making is at the heart of effective workforce planning. By leveraging workforce analytics and performance data, organisations can make informed choices that support their strategic business planning process. Workforce planning should also be viewed as a continuous process, with regular reviews and updates to ensure ongoing alignment with business goals.
Prioritising diversity, equity, and inclusion within workforce planning efforts is another best practice, as a diverse workforce brings a broader range of perspectives and skills to the organisation. By following these principles, organisations can ensure their workforce planning efforts deliver strategic value, support business planning, and drive long-term business success.
Workforce planning as a strategic HR instrument
Workforce planning strategy transforms HR from reactive recruitment to strategic talent leadership. By harnessing proven models, like scenario planning and skills gap analysis, and powering them with integrated workforce planning tools and services, organisations can control costs, boost productivity, and build agility.
Zalaris enables this transformation and unlocks the benefits of workforce planning with a comprehensive portfolio of services and products which centralise processes across regions, ensuring compliance while reducing administrative effort. Combined with advisory support and HR shared services expertise, we provide end-to-end HR and Payroll consulting and services that enable organisations to align workforce strategy with business goals.
For leaders seeking to future-proof their workforce, the time to act is now. Get in touch with our team and turn planning into measurable performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is strategic workforce planning and how does it differ from traditional HR planning?
Strategic workforce planning is a proactive approach that aligns talent strategies with long-term business objectives. Unlike traditional HR planning, which addresses immediate staffing needs, strategic workforce planning anticipates future skills requirements and prepares for industry changes to ensure organisations have the right people with appropriate capabilities when needed.
2. Which workforce planning models work best for mid-sized companies?
Mid-sized companies typically benefit from Supply and Demand Forecasting Models and Skills Gap Analysis Models. These approaches compare future labour requirements with projected workforce availability whilst identifying current capability shortfalls. Scenario Planning Models also prove valuable for preparing different business outcomes without requiring extensive technology infrastructure.
3. How can HR teams measure the success of their workforce planning initiatives?
HR teams should track key performance indicators including time-to-fill critical roles, internal promotion rates, and skills gap closure percentages. Additional metrics encompass employee retention rates in key positions, succession planning pipeline strength, and workforce cost per revenue. Quarterly reviews against business objectives demonstrate effectiveness and highlight improvement areas.
4. What technology tools are essential for effective workforce planning in 2025?
Essential workforce planning technology includes Human Capital Management systems with analytics capabilities, workforce analytics platforms that transform HR data into insights, and scenario planning software for modelling business outcomes. Cloud-based solutions provide particular value through real-time data access, predictive analytics, and integration with existing business systems.
5. How should organisations address skills gaps identified through workforce planning?
Organisations should combine internal development with targeted recruitment to address skills gaps. Conduct skills assessments to understand gap urgency, implement reskilling programmes for existing employees, and develop partnerships with educational institutions. For critical gaps, consider contract specialists whilst building internal capabilities through clear career progression pathways and mentoring programmes.
Related content

Liam Clark
HCM Consultant
Liam is an HCM Consultant of Zalaris UK&I, with a technical and functional background of SAP Products. His current focus is on SuccessFactors Employee Central and Recruitment Modules. Before joining Zalaris at the start of 2021, he worked as a SAP HCM and Payroll Specialist within the UK Public Sector.
Table of Contents
- What is workforce planning, and why is it important?
- Traditional vs strategic workforce planning
- Why does workforce planning matter?
- Workforce planning foundations: Models, frameworks, and the planner
- The models
- The role of the workforce planner
- Creating a strategic workforce planning framework: A practical lesson for workforce planners
- Turning framework into action: Best practices for the workforce planner
- Gap analysis: Identifying workforce needs and priorities
- Workforce planning tools: Increasing efficiency through technology
- Human Capital Management (HCM) suites:
- Workforce analytics platforms:
- Scenario and forecasting tools:
- Employee retention: Building a resilient workforce
- Action plan: Turning workforce planning into results
- Overcoming challenges in workforce planning
- Best practices for effective workforce planning
- Workforce planning as a strategic HR instrument
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)

