Transform Business with SAP Master Data: A complete guide
In business, data is king. Companies rely on precise and up-to-date information for digitalisation to optimise business processes and make informed decisions.
Liam Clark

Imagine harnessing your data not just to streamline operations but to significantly enhance productivity and drive business excellence.
SAP master data is the critical foundation underpinning every SAP implementation, playing an indispensable role in enabling efficient and seamless digital transformation initiatives, particularly within human resources.
In this comprehensive guide, we will define SAP master data, explore its strategic importance for enterprises, and demonstrate how it can be leveraged to successfully execute digitalisation strategies.
From precise data capture and centralised management to ongoing maintenance and optimisation, we will present industry best practices to maximise the value of your SAP master data central management efforts.
What is SAP master data?
SAP master data comprises fundamental business-relevant information that is rarely, if ever, changed and is essential for a company. It is captured in the SAP system and serves as the basis for many business processes. There are two main types of master data: primary and secondary.
Primary master data
Primary master data in SAP refers to employee master data, customer master data, vendor master data, location master data, product master data, and asset master data. These master data domains play a vital role in ensuring accurate and consistent information across business operations and manufacturing processes.
Maintaining master data with high data accuracy and governance workflows helps prevent poor data quality that can disrupt business processes. SAP master data central management enables organisations to consolidate master data records from multiple systems, including non-SAP systems and third-party applications, into a central hub. This central governance approach enforces business rules and policies, ensuring governed master data is reliable and compliant across the enterprise.
1. Employee master data
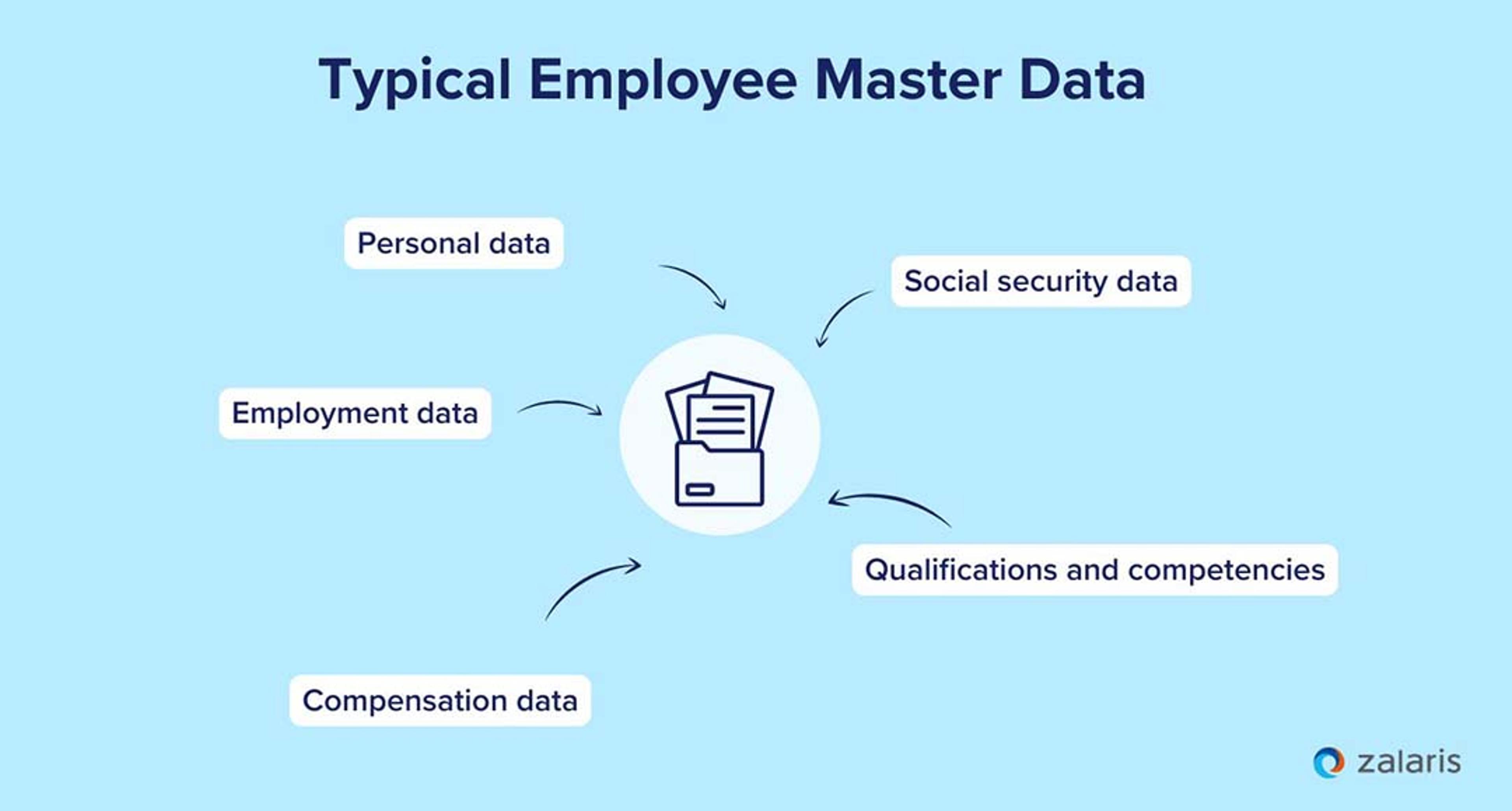
Employee master data includes basic and unchangeable information about a company's employees, essential for managing and organising human resources.
Typical employee master data includes:
- Personal data: Name, birthdate, address, contact details.
- Employment data: Start date, department, position, contract type.
- Compensation data: Salary, bonuses, bank details.
- Social security data: Social security number, tax class.
- Qualifications and competencies: Educational qualifications, work experience, certificates.
This type of master data is rarely changed but forms the basis for many HR processes such as payroll, performance reviews, and statutory reporting.
2. Customer master data
Customer master data includes essential information about customers, such as name, address, contact details, and other relevant details necessary for a business relationship.
3. Supplier master data
Supplier master data contains information about a company's suppliers, including company name, address, contact details, and contract terms for procuring goods or services.
4. Location master data
Location master data describes the various locations of a company or organisation. This data can include location names, addresses, geographical coordinates, and specific information about the functions or services at each site.
5. Product master data
Product master data includes basic information about the products or services offered by a company. This includes product descriptions, item numbers, pricing information, dimensions, and other specific characteristics.
6. Asset master data
Asset master data includes information about a company's assets and machinery, including location, technical specifications, maintenance schedules, and maintenance history.
Secondary master data
Secondary master data is less common and often supports primary master data. Typical examples include:
1. Conditions
Pricing tiers, discounts, payment terms specific to customers or suppliers.
2. Classifications
Hierarchical structures or groupings used to organise master data.
Data landscape: The difference between transactional and inventory data
Unlike master data, transactional data constantly changes and captures dynamic transactions and events within a business process. They document what happens in the company, such as the timing of a product sale or invoice payment. Transactional data, due to its frequency, provides a current insight into a company's operational activities.
Inventory data, on the other hand, offers a detailed overview of the current state of goods or materials at a specific point in time. It indicates how many products are in stock, which orders are still pending, or which materials are available. This data is crucial for inventory management and planning procurement and production processes.
Why is SAP master data important for businesses?
SAP master data helps businesses address key issues and make informed decisions. It also offers further benefits for HR master data management, such as:
Efficient personnel management and development
A centralised management system enables more efficient management and analysis of human resources. This facilitates processes such as tracking qualifications, training, and career development, supporting targeted personnel development and planning.
Improved recruitment processes
SAP master data optimises recruitment processes. A centralised system makes it easier to manage applicant data and automates the hiring process, enabling quicker identification of suitable talent. This speeds up the hiring process and improves the quality of new hires.
Automation of payroll and compensation management
SAP master data allows efficient and error-free payroll by centrally managing all relevant employee information such as salary data, bonuses, and deductions, enabling the entire process to be automated.
Management of employee benefits and incentives
A central master data system also facilitates the effective management of employee benefits and incentive programs. It supports tracking of holidays, health insurance, pension plans, and other benefits, contributing to employee satisfaction and motivation.
Facilitating compliance with labour laws
SAP master data helps the HR department comply with labour laws. By capturing and maintaining all relevant employee data centrally, audits can be conducted more efficiently, and the risk of non-compliance is minimised.
Other key benefits include:
- Reduced errors and data redundancies
- Improved analysis capabilities for data-driven decisions
- Increased transparency
- Targeted optimisation of business processes for efficiency gains
3 best practices for successful master data management and data quality
For an effective master data management strategy, innovative software solutions like SAP Master Data Management (MDM) are utilised to enable all stakeholders to make reliable, data-driven decisions and respond quickly to new events.
Here are some best practices to optimise your HR master data management strategy:
1. Standardise and centralise data
One of the most important best practices in master data management is standardising and centralising HR data. Implementing uniform data formats and a central data storage ensures that all HR data is consistent and easily accessible. This reduces redundancies and inconsistencies, improves data quality, and facilitates access to up-to-date information. Tools like SAP MDM can help automate and optimise these processes.
2. Regularly review and cleanse data
To ensure the integrity and accuracy of master data, regular data review and cleansing is essential. This involves identifying and correcting errors, duplicates, and outdated entries. A systematic approach to data cleansing helps increase the reliability of HR master data, ensuring that decisions are based on solid data. Automated tools can make this process more efficient and reduce manual work.
3. Employee training and awareness
For a master data management strategy to succeed, all stakeholders must understand the importance of high-quality data. Regular training and awareness campaigns can help employees recognise the significance of data quality.
SAP master data as a step towards digital transformation in HR
Managing SAP master data effectively is vital for companies scaling up with increasing data volumes. By adopting intelligent software solutions such as SAP Master Data Management (MDM), along with automated tools and AI technologies, businesses can simplify the complexities of digital transformation.
Unlock the full potential of your HR processes with SAP master data. Embracing these strategies will drive efficiency, enhance decision-making, and ensure compliance. By streamlining your data management, you pave the way for a more agile and responsive business environment, ultimately boosting productivity and operational excellence.
Your journey to a streamlined, data-driven business starts now. For more insights on leveraging SAP master data to achieve your HR goals, reach out to us today
Discover how Zalaris can be your trusted partner in this transformation, guiding you every step of the way to achieve unparalleled success in your HR operations.
FAQ
Related content

Liam Clark
HCM Consultant
Liam is an HCM Consultant of Zalaris UK&I, with a technical and functional background of SAP Products. His current focus is on SuccessFactors Employee Central and Recruitment Modules. Before joining Zalaris at the start of 2021, he worked as a SAP HCM and Payroll Specialist within the UK Public Sector.

